Avaada Electro credit ratings reaffirmed by ICRA
ICRA has reaffirmed its credit ratings for Avaada Electro Ltd (AEL) and assigned ratings for enhanced borrowing limits, factoring in the company’s rapid scale-up in solar manufacturing and continued support from its parent, Avaada Ventures.
India’s 2025 renewable energy sector review: Key highlights and way forward
With record 40+ GW solar and wind installations (solar: 34.9+ GW, wind: 5.8+GW), 2025 has marked yet another high point in Indian annual renewable capacity additions. The capacity additions have been driven by strong project momentum across all solar segments.
Bridging the gap between India’s rare earth reserves and extraction challenges
While India has research capabilities across public laboratories and academic institutions in both rare earths and battery recycling, the transition from lab-scale innovation to industrial deployment has been slow. This gap between research and commercial execution continues to limit scale across the critical minerals ecosystem.
India’s energy transition has shifted gears decisively
India is moving decisively beyond capacity addition toward system-level maturity. Expanded transmission planning, a more diversified energy mix and better regulatory clarity signal a market design that is becoming ever more dynamic and future ready.
Global solar generation topped 540 GW in April, says Solcast
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that the global peak of solar output in 2025 occurred on April 29, at 06:00 UTC, estimated at 539 GW.
Top 5 trends shaping India’s battery energy storage systems market in 2025
India’s battery storage landscape is undergoing a decisive transformation in 2025. Across utilities, regulators, and developers, BESS has moved beyond early-stage exploration and is increasingly recognized as an essential component for grid stability, renewable integration, and long-term energy planning.
AGEL tops Global Green Utilities Rankings by UK-based Energy Intelligence
Adani Green Energy Ltd (AGEL) has claimed the top spot in the latest Energy Intelligence Top 100 Green Utilities ranking, pushing past China’s National Nuclear Corp. and Spain’s Acciona.
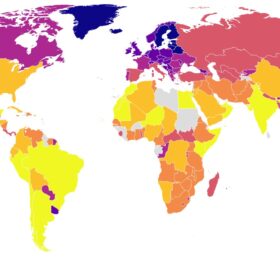
“Waaree well positioned as trusted solar partner under Europe’s NZIA Regime”: Sunil Rathi
Waaree Energies is looking to deepen its presence in Europe as the European Union’s Net-Zero Industry Act (NZIA) reshapes solar procurement and curbs reliance on Chinese module suppliers. “As a listed, Tier-1, bankable manufacturer with a proven multi-gigawatt track record, we offer the scale and credibility European developers now prioritise,” says Sunil Rathi, executive director, Waaree Group.
Why Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities will drive India’s next big solar jump
Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities are no longer behind in the solar journey, they are becoming the main growth drivers. With better government support, easier net-metering rules, and more awareness about savings, people in smaller cities are now ready for rooftop solar in a big way.
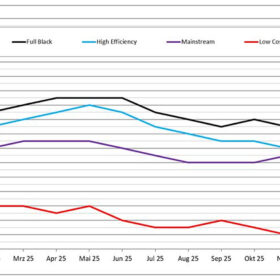
Too much to choose from, too little to decide
Market pressure in the solar and storage sectors often favors low-cost solutions, but long-term success depends on balancing price, quality, and reliability for assets designed to operate for decades. Numerous examples, from low-grade silicon modules to residential hydrogen and redox flow storage, show how technically ambitious products can fail when costs, complexity, or durability are misjudged.