Since 2014, around 29 GW of utility scale solar tenders have been issued in India. Most of this capacity (81%, 23.5 GW) has been tendered by NTPC, SECI, DISCOMs and other public sector entities for project development by the private sector. But there is also a sizeable 19% (5.5 GW) tendered in the form of EPC contracts, where capital investment will be made by NTPC and other public sector companies including state government-owned generating companies (for example, KREDL, APGENCO).
It is interesting to note that actual progress on these two types of tenders is very different. For project development tenders, 36% (8.5 GW) of total issued capacity has been commissioned and 7% of the capacity has been cancelled. In contrast, for EPC tenders, only 18% (930 MW) has been commissioned and as much as 29% stands cancelled.
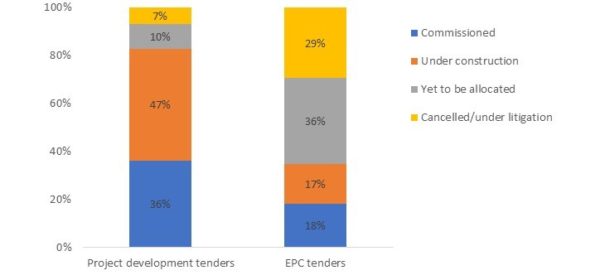
Figure: Status of projects under project development and EPC tenders issued since 2014
The poor progress in EPC tenders is as predicted by us last year. Despite that, public sector companies continue to bring out more EPC tenders – more than 50% of new tenders issued in Q3 2017 were structured as EPC contracts.
- Power from EPC tender based projects is significantly more expensive than from project development tenders;
- Most EPC tenders issued by public sector companies face long or indefinite delays in allocation;
- Participation of state-owned companies at a time of aggressive competition among private companies is difficult to understand;
As against an average 2-5 months taken between announcement and allocation of project development tenders, allocation of EPC tenders by public sector companies has taken an average of 6-8 months. Some of these tenders including NLC Tamil Nadu 500 MW and NLC Odisha 250 MW were issued almost a year ago but they have not yet been allocated. Moreover, some tenders including CIL 200 MW and KREDL 200 MW have been issued, cancelled and subsequently reissued with modified requirements. The frequent cancellations as well as delays reflect low market interest for such tenders.
EPC tenders from public sector companies stipulate more stringent technical specifications resulting in higher execution costs (and presumably, better quality). Moreover, many EPC tenders have domestic content requirement (DCR) stipulation again resulting in 5-7% extra capital expenditure. Higher capital expenditure coupled with conservative financial assumptions means that the final tariff offered to the DISCOMs is about 20-30% higher than that offered by private sector developers, who are willing to make more aggressive operating and financial assumptions. DISCOMs are understandably not too keen on buy such power.
Perhaps because of slow progress in EPC tenders, we have observed a strange practice where public sector companies are now bidding aggressively against private sector competitors in project development tenders. Recent cases include NLC winning 709 MW capacity in the Tamil Nadu 1,500 MW tender and GIPCL and GSECL together winning a total of 150 MW in the GUVNL 500 MW tender. As per our estimates, expected returns for both these tenders are significantly below market expectations.
There was a strong public sector role envisaged in development of solar projects back in 2013/14, when capital costs were much higher and investment appetite of private sector was not established. Today, when there is ample private capital available for the solar sector at very attractive terms and when there is a slowdown in tender issuance, there is absolutely no justification for public sector to crowd out private investments. The government needs to rethink the role of public sector companies in clean energy sector.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own, and do not necessarily reflect those held by pv magazine.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.