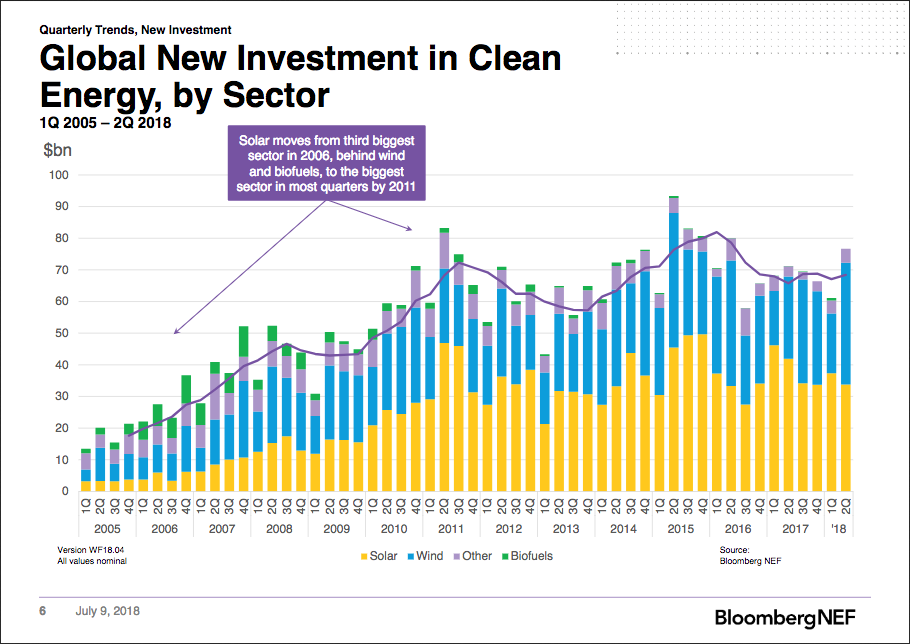
Wind and energy smart technologies, like electric vehicles and batteries are attracting increasing shares of the clean energy investment pie, with wind snapping up US$57.2 billion of the $138.2 billion invested in 1H 2018 – a 33% increase on the previous year – and energy smart technologies receiving $5.2 billion, up 64%.
While solar’s share is still substantial, at $71.6 billion, it saw investment fall 19% YoY, due to both “significantly” lower capital PV project costs, which result in less cash spent per MW installed; and China’s reductions to its PV feed-in tariffs and capacity allowances.
Out of the top 10 top investments, solar comprised the second largest – $881 million in debt for the 110 MW EIG Atacama 1STEG plant in Chile – and the second last – $112 million in VC- Series B / Second round to scale C&I finance solutions.
The China effect
Looking at China specifically, which accounts for the largest share of solar investments, finances dropped 29% from 1H 2017, to $35.1 billion. The second half of this year is expected to show the full effects of the decision, however, which include new global capacity additions falling for the first time in solar’s record.
Pietro Radoia, senior solar analyst at BNEF, commented, “It [the policy change] will also mean overcapacity in solar manufacturing globally, and yet steeper price falls.
“Before the Chinese announcement our team was already expecting a 27% fall in PV module prices this year. Now we have revised that to a 34% drop, to an end-2018 global average of 24.4 U.S. cents per watt.”
He added to pv magazine, “We anticipate a 22% PV supply glut even after polysilicon producers reduce their utilization rates and possibly halt of some less competitive capacity due to the sluggish demand.”
Regarding projects, Radoia told pv magazine that BNEF has seen project developers postponing and renegotiating their contracts, on the back of expectations that module prices will fall further.
“We heard of developers locking into $0.27/W module contracts for delivery in 3Q and 4Q in India and EU even before the policy headwinds in China. 4Q 2018 might turn out to be a hot market in terms of contract negotiations,” he said.
Overall, clean energy investment slipped 1% in the first six months of 2018, compared to the previous year, Q2 saw figures rise 8% to $76.7 billion. The top five investors, by country, were: China, the U.S., Europe, India and Australia.
Look out for a Q&A between pv magazine and BNEF on the current solar module situation, tomorrow.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.