The world of photovoltaic solar energy is rapidly evolving, and at the forefront of this transformation is the International Energy Agency (IEA) Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme (IEA PVPS), a collaboration of hundreds of experts across academia, governments and industry. Task 1 of the IEA PVPS focuses on Strategic PV Analysis and Outreach. For 30 years, the Trends in PV Applications Report offers a comprehensive view of the PV market, policies and key industry developments globally, and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. It is designed to assist those who are responsible for developing the strategies of businesses and public authorities, and to support the development of medium-term plans for electricity utilities and other providers of energy services. It also provides guidance to government officials responsible for setting energy policy and preparing national energy plans. has been recently published.
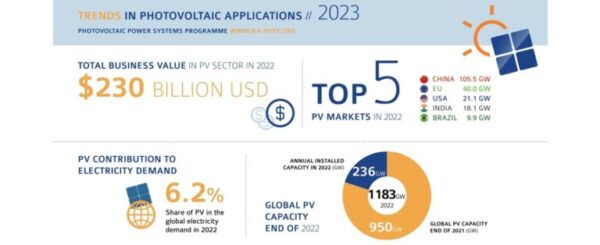
Image: IEA-PVPS
Market Volumes: A Symbolic Milestone
As the PVPS Trends report reveals, the PV industry has achieved a significant milestone, crossing the 1-terawatt (1 183 GW) cumulative capacity mark. This achievement marks a symbolic turning point in the journey towards sustainable energy. Two thirds of all existing PV plants have been installed in the past 5 years.
In 2022, the annual capacity reached an impressive 235.8 GW, a new record, which could have been even higher, with grid connection issues and lack of installers slowing down the development of PV in numerous locations. Notably, China contributed 45% of this capacity, with the European Union following at 17%. The growth was not limited to these regions alone, as strong expansion was witnessed globally, with a 35% increase in annual capacity compared to 2021. Entering the list of the Top 10 annual PV markets wasn’t solely confined to large countries or populations, as demonstrated by the Netherlands, which installed more than 3.9 GW of capacity (see Figure 2). However, the PV market is still concentrated in a dozen of countries globally, with a lot of additional potential for market development.
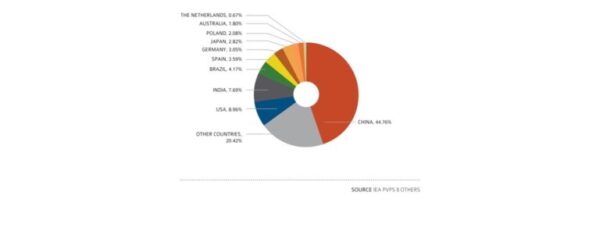
Image: IEA-PVPS
The report shows that PV capacity was evenly spread between distributed and centralized systems, despite variations in different countries and regions. Some countries, (India, the USA, Spain), showed a dominance of centralized systems, while China exhibited a more balanced distribution. Recently developed markets continue to start with utility-scale development while regulations for distributed systems are more complex to put in place. While the global PV market was on an upward trajectory, some countries experienced slowdowns due to supply issues, grid congestion, and labor shortages. These challenges are expected to persist in certain regions, emphasizing the need for strategic planning to address these issues.
Competitiveness Amidst Challenges
Because of the high cost of electricity in Europe and other locations, caused by events including the Ukraine war, the competitiveness of PV continues improving. Some support mechanisms, for example contract-for-difference arrangements, generated revenue for state governments, buoyed by these high electricity market prices. The Trends report also highlights the continued growth of prosumers (consumers, who are producing part – or all – of their own electricity consumption) policies, underlining the resilience of the PV market.
Industry Investments and Challenges
The PV industry witnessed significant investments in new silicon, cell, and module manufacturing capacity, with at least 700 GW of module manufacturing capacity. Governments around the world (USA, Europe, China, India) are actively supporting local manufacturing and trade conflicts and labor concerns are influencing manufacturing support. The rapid scaling of manufacturing outpaced market development, which resulted in significant module price drops in 2023 due to massive oversupply. With markets developing slower than needed, overcapacities in the industry will cause significant damages to many players and delay the roll out of much needed local manufacturing.
Social acceptance and grid Capacity: two Growing Concerns
As PV volumes surge, grid capacity is becoming a concern in some countries. While some nations are responding with substantial investments in transmission infrastructure, others are using curtailment and other measures at the distribution level. This comes in parallel with increased social acceptance, mostly related to centralized systems, issues which are delaying PV uptake in several key countries.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future Together
The IEA PVPS Trends Report not only provides valuable insights into the current state of the PV industry but also highlights the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. As we celebrate the symbolic milestone of 1 TW of cumulative capacity, market development to reach climate change goals needs more support from policymakers and energy stakeholders. With a wider gap between market and production, a period of lower prices might accelerate PV development, while challenges remain numerous to ensure long term development.
This article is part of a monthly column by the IEA PVPS programme. It was contributed by IEA PVPS Task 1 – Strategic PV Analysis & Outreach. Further information can be found in Task 1’s new Trends in PV Applications 2023 report.
By Gaëtan Masson, Melodie de l’Epine and Bettina Sauer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own, and do not necessarily reflect those held by pv magazine.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.