An SBICAPS report expects India to increase its energy storage capacity 12-fold to 60 GW by FY 2032, outpacing the already impressive growth pencilled in for RE sources. The report adds that the evolving landscape of RE tenders reflects this trend, with a substantial uptick in the proportion of projects incorporating storage solutions, from 5% in FY 2020 to 23% in FY 2024.
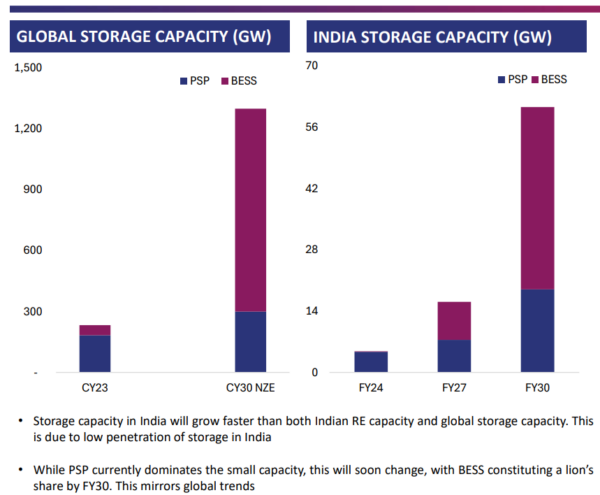
While pumped storage projects (PSPs) currently dominate the small energy storage capacity, BESS will constitute a lion’s share by FY 2030, helped by their locational flexibility, promise of technological improvements dipping tariffs further, improving discharge characteristics, and rapid response time. BESS will surge 375 times to 42 GW by FY 2032, from FY 2024 levels, as per the report.
The report says that developing the BESS ecosystem in India presents a vast funding opportunity, both at project level and for the upstream level. The sector is set for a boom across the value chain – from BESS projects, to cell manufacturing, down to components of cells. This would be aided by helpful government directives on waiver of interstate transmission charges and energy storage obligation (ESO)/renewable purchase obligation (RPO) trajectory creating a steep trajectory for DISCOMs to adhere to, the latter boosting demand.
Funding of the BESS ecosystem presents an INR 3.5 trillion opportunity till FY32, with an INR 800 billion medium-term kicker provided by upcoming cell manufacturing capacities, adds the report.
The report states lenders funding BESS projects should consider critical variables such as the presence of a firm PPA/PSA agreement from a credible DISCOM, project model (co-location/standalone), and cell technology in use.
Despite their long gestation period, asset life-power purchase agreement (PPA) period mismatch exacerbating stranded asset risks, and time-consuming clearance processes, PSPs too will see a stellar growth owing to their low variable operating costs, absence of e-waste, and ability to generate reactive power which improves grid stability. These will primarily be used for peak shaving. PSPs will grow four times to 19 GW by FY 2032, from FY 2024 levels.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.









By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.