In India, 127 companies have committed to net-zero through science-based target initiative (SBTi) and only 7% of these companies hail from high emission sectors like power, cement, metal and mining. The rest belong to sectors like textiles, software and services, typically considered to be having low to medium level of carbon footprint, reveals ICRA ESG Ratings’ report on SBTi commitments by Indian companies.
SBTi is a voluntary target-setting initiative whereby companies can commit to setting science-based targets and have their objectives independently assessed and validated. Commitments and target taking are done through stated sector wise guidelines by SBTi. The initiative has guidelines for setting emission reduction targets for various sectors.
The United Kingdom leads globally with the highest number of companies committed to SBTi net-zero targets. In contrast, China, despite being the largest emitter, has a lower share of companies with such commitments.
India ranks sixth globally with 127 companies in the nation committing to net-zero targets.
The ICRA report states power, cement, metal and mining are high-emission sectors contributing 55% to India’s overall emissions. However, 127 companies committing to SBTi net-zero targets are primarily from non-hard-to-abate sectors like textiles, software, and pharmaceuticals.
Overall, around 25 companies from the power, cement, and mining sectors have committed to emission reduction through SBTi. This includes companies specifically targeting net-zero emissions too.
The report states that within the power sector, only six Indian companies have adopted SBTi, with three of them from the renewable energy space. Among the companies with SBTi targets, only Adani Energy Solutions has managed to reduce absolute emissions by 11% in the last six years by transitioning towards renewable energy and adopting energy efficiency measures.
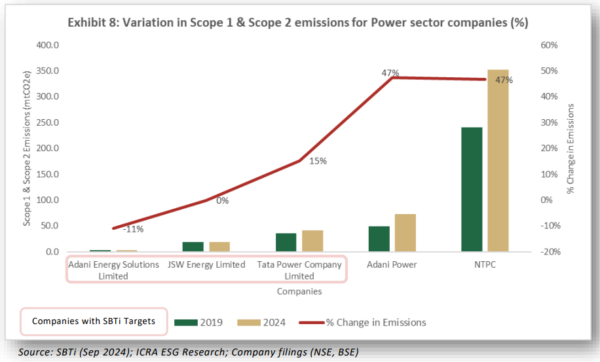
JSW Energy, with a capacity of 6,677 megawatt (MW) witnessed no change in absolute emissions due to its efforts towards renewable energy expansion, carbon capture initiatives, implementation of waste heat recovery systems, etc.
With a capacity of 14,707 MW, Tata Power Ltd., which has a self-declared net-zero target, witnessed a 15% increase from FY2019 to FY2024. “This was aligned with the industry trend, resulting from increasing production capacities and demand for electricity and power across the nation,” stated the report.
In the cement sector, of the eleven companies with SBTi commitments, ACC Ltd has been successful in reducing its emission intensity by 11% over 2019–2024, resulting from a decline in absolute emissions during the same period. The decline in emission is primarily driven by adoption of renewable energy, utilisation of green energy techniques, producing low-carbon cement, and implementing carbon capture technologies, among others.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.