From pv magazine Australia
A new paper co-authored by Australian National University Prof. Andrew Blakers examines how long-duration pumped hydro energy stations (PHES) could provide 95% of global energy storage for the electricity industry, with the storage capacity of 2 trillion electric-vehicle batteries. These systems could be game changers for the world’s energy storage needs if combined with batteries.
Blakers noted in a recent LinkedIn post that PHES systems last over 100 years, require no new dams on rivers, have minimal land and water requirements, and involve little mining.
“PHES has far lower capital cost than batteries (which excel for short term storage). Together, PHES and batteries solve energy storage,” said Blakers.
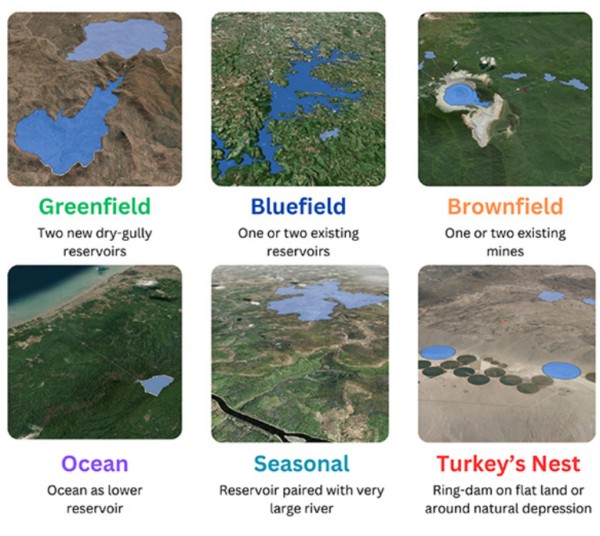
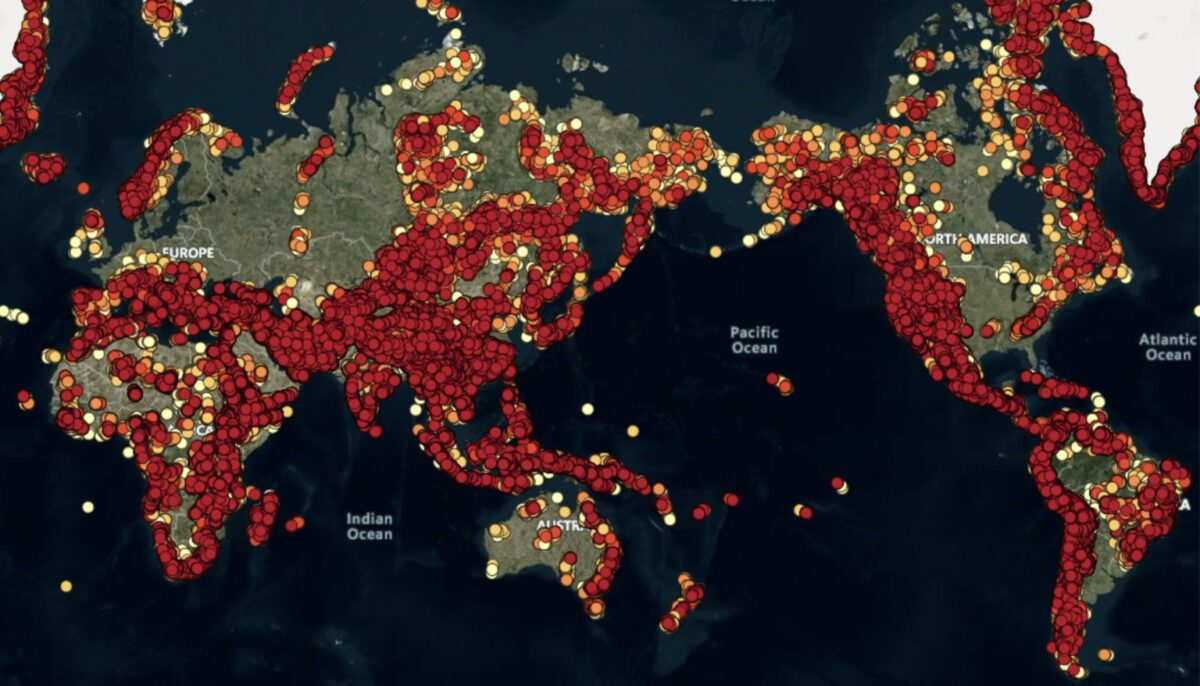
The paper – “Pumped hydro energy storage to support 100% renewable energy,” which was recently published in IOP Science – discusses the Global PHES Atlases developed by Australian National University. These atlases identify 0.8 million off-river (closed-loop) PHES sites with a combined 86 million GWh of storage potential, which is equivalent to about three years of current global electricity production.
“Long-duration energy storage is required to support future solar-dominated energy systems,” said the researchers. “On a global basis, and for most regions, the PHES resource is two orders of magnitude larger than the likely future storage requirement of affluent, ‘electrified’ and decarbonized people. This means that energy planners can deploy large-scale solar and wind projects with confidence in the knowledge that there is at least one highly credible storage solution.”
Off-river PHES sites identified in the Global PHES Atlases do not require expensive measures to cope with major floods or the need to dam more rivers.
“These attributes mean that the cost estimates and perceptions developed for river-based hydroelectric systems generally do not apply to premium off-river PHES systems,” said the researchers.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.







By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.