‘Cool roofs’ increase power yield in bifacial rooftop PV systems
A Spanish-Algerian reserch group has tested how “cool roofs” could help increase power yield in rootop bifacial PV systems. Cool roofs are based on coating materials with high reflectance properties.
Agrivoltaic system achieves 9.9% efficiency, LCOE of $0.033/kWh
Researchers in China have built a prototype of a spectral-splitting concentrator agrivoltaic system (SCAPV) with a PV efficiency of 9.9, a hybrid light-use efficiency rating of 9.05%, and a levelized cost of energy (LCOE) of $0.033/kWh.
Residential PV for urban loads as an antidote to solar curtailment
Researchers in the Netherlands have proposed the use of residential PV capacity to supply electricity to urban loads such as tram substations and dwellings, potentially reducing PV curtailment and demand for additional storage.
Researchers shed light on mysterious, higher energy yields in vertical PV systems
Scientists in the Netherlands have sought to understand the reason for unexpected gains in vertical PV systems and found that these installations have a much higher heat transfer coefficient than their horizontally deployed counterparts.
Sharp claims 33.66% efficiency for silicon tandem solar cell
The Japanese electronic manufacturer said this is the world’s highest efficiency for a stacked solar cell that combines a tandem double-junction solar cell and a silicon solar cell.
New lead-free perovskite solar cell design promises 26.96% efficiency
Bangladeshi scientists have developed a high-efficiency perovskite solar cell with 26.96% efficiency, an open-circuit voltage of 1.0478 V, and a fill factor of 81.35%.
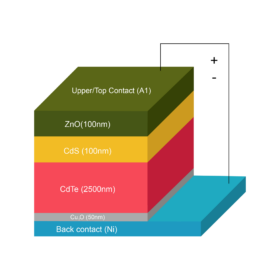
Novel cadmium telluride solar cell design with potential efficiency of 31.82%
Scientists in Bangladesh designed a cadmium telluride solar cell with upper/top and back contact materials made of aluminum (Al) and nickel (Ni). The device reportedly showed a quantum efficiency of around 100 % at visible wavelengths.
Fraunhofer ISE presents silicon carbide string inverter for medium-voltage applications
Fraunhofer ISE researchers claim the new silicon carbide inverter is technically able to handle voltage levels of up to 1,500 V at 250 kVA in utility scale solar power plants.
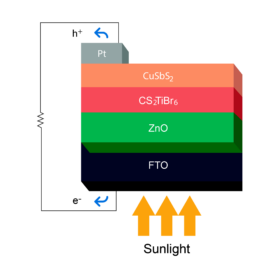
Hong Kong researchers develop inverted perovskite solar cell with 25.6% efficiency
The research team said the cell also achieved remarkable thermal stability, as it was able to retain 90% of its original efficiency for over 1,000 h. The device uses a self-assembled monolayer to stabilize the interface between the perovskite absorber and the hole transport layer.
Europe may go back to ‘normal’ inventory levels by June 2024
pv magazine recently spoke with Bartosz Majewski, CEO of Menlo Electric, a Poland-based solar distributor operating in Europe, about high inventory levels of solar panels in Europe.