Optimizing residential PV-driven heat pumps with lithium-ion batteries reduces LCOE by 7%
Scientists in Spain have simulated the combination of power-to-heat-to-power storage systems with lithium-ion batteries to supply energy needs and heat pump production of an electrified dwelling. PV self-consumption was found to increase by up to 20% and levelized cost of energy decrease by 7%.
How to reconfigure PV modules in degraded solar plants
Indian scientists have developed six different strategies to reconfigure solar modules in degraded PV assets. Their analysis showed which conditions make the reconfiguration of an underperforming solar plant profitable.
PV module recycling tech based on electrohydraulic shockwave fragmentation
An international research team has developed a new machine that utilizes shockwaves to separate the different materials of a solar PV module. Chemical processes can be further used to extract silicon and silver. Results show the recovery of more than 99.5% of the original weight of the panels.
Japanese energy supplier to use green hydrogen for district heating, power
Akasaka Heating & Cooling Supply says it will use green hydrogen produced at an unspecified location in Japan to produce heat and electricity for its Akasaka 5-chome district heating system in central Tokyo.
Cadmium telluride vs. crystalline silicon in agrivoltaics
Researchers in Canada have compared strawberry growth under uniform illumination from semi-transparent thin-film cadmium telluride panels and non-uniform illumination from semi-transparent crystalline silicon modules. Their analysis considered metrics such as fresh weight, height, leaf count, chlorophyll content, soil temperature and humidity.
Viridian Solar launches 23.6%-efficient TOPCon BIPV panel
The UK company says the new modules have a rated power output of 445 W and can reportedly guarantee a power yield of 95% after 10 years.
Fronius introduces 15.8 kWh lithium iron phosphate battery for rooftop PV
The Austrian manufacturer has launched its first battery system using LFP cells. A total of up to four units can be connected in parallel for a capacity of 63 kWh.
Exide releases mobile 200 kWh, 400 kWh storage solutions
The company said the new product uses up to four lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries. It is equipped with a single 180 kW or 2 x 90 kW chargers and multiple three-phase sockets.
New research shows correlation between PV module electrode corrosion and damp heat test
New research shows correlation between PV module electrode corrosion and damp heat test
A research group in Japan identified a correlation between damp heat test of 1,000 hours to 3–6 years of field exposure in humid areas and changes in acetic acid concentration in photovoltaic modules. Their analysis also showed that an acetic acid concentration over 10,000 μg/g can be critical.
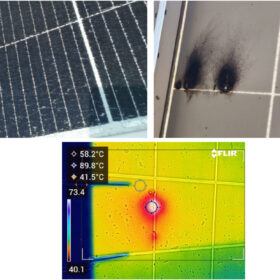
New study shows reducing number of solar modules per string reduces risk of hotspots
Scientists in Indonesia have investigated early operational defects in a 24.9 MW solar PV system in Sumatra and have identified hotspot formation as the dominant defect. They also detected 282 cases of glass cracking, 350 cases of junction box failures and shading effects linked to module defects.