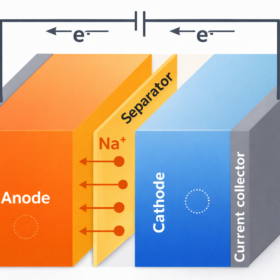
Sodium-ion batteries now competitive in niche markets
Sodium‑ion batteries are emerging as a safer, lower-cost alternative to lithium‑ion, with a recent international study highlighting their competitiveness in stationary energy storage. The research shows that ongoing investment and supply-chain development could enable broader adoption within the next decade.
India’s Union Budget 2026–27 removes customs duty on solar glass inputs, lithium battery cell machinery, and critical minerals processing equipment
India’s Union Budget 2026–27 extends basic customs duty (BCD) exemptions on the import of capital goods used for lithium-ion cell production for battery energy storage systems (BESS), as well as capital goods required for processing critical minerals. It also removes the 7.5% BCD on sodium antimonate used in solar glass manufacturing.
Luminous Power inaugurates 500 MWh lithium-ion battery assembly line at Baddi facility
Luminous Power Technologies has inaugurated its first lithium-ion battery assembly line at Baddi, Himachal Pradesh. This new line is designed to produce standalone lithium-ion battery packs, stationary battery energy storage systems (BESS), and automotive battery packs for e-rickshaw applications.
Oswal Greenzo Energies secures India’s first port-based 5 MW green hydrogen project at Deendayal Port, Kandla
Oswal Greenzo Energies, a joint venture between Oswal Energies Ltd and Greenzo Energy India Ltd, has been awarded a contract for the design, supply, installation, testing, and commissioning of a 5 MW green hydrogen plant at Deendayal Port, Kandla. The facility will be India’s first green hydrogen plant located at a major port, positioning Deendayal Port as an early mover in maritime decarbonisation.
EU installs 27.1 GWh of battery storage in 2025 as utility scale leads
The European Union added 27.1 GWh of battery energy storage capacity in 2025, with utility-scale systems accounting for the majority of new installations as residential storage declined amid lower electricity prices and reduced support schemes, according to a new report from SolarPower Europe.
Electrolyser selection and balance-of-plant engineering for renewable integrated hydrogen projects
Green hydrogen will scale not through isolated technology breakthroughs, but through disciplined engineering execution. Projects that embed electrolysers within robust, flexible, and future-ready Balance-of-Plant architectures will define the next phase of industrial decarbonisation and renewable energy integration worldwide.
India requires $145 billion in annual energy investment to bridge growth and climate targets
India must mobilise around $145 billion in annual energy investment to sustain economic growth while pushing its net-zero ambitions. The bulk of this capital will be directed toward scaling up renewable power generation, grid infrastructure modernization, and energy storage, according to Wood Mackenzie.
Renewable energy industry’s key expectations from Union Budget 2026
The upcoming budget must prioritize in-house technology and equipment development, provide clarity on delayed power purchase agreements (PPAs) and power sale agreements (PSAs), increase budgetary allocation and policy support for Green Energy Corridors, introduce production-linked incentives for battery energy storage system (BESS) manufacturing, establish an Approved List of BESS Integrators (ALBI), lower the cost of capital through priority sector lending, extend ALMM for solar cells, and continue the ISTS waiver, among other measures.
Scientists design low-cost sodium-ion battery with cheap electrode materials
Conceived for stationary energy storage, the proposed sodium-ion battery configuration relies on an P2-type cathode material and an hard carbon anode material that reportedly ensure full-cell performance. Electrochemical testing revealed initial capacities of 200 mAh/g for the cathode and 360 mAh/g for the anode with capacity retentions of 42% and 67.4% after 100 cycles.
Pre-Budget 2026: Solar and storage industry calls for tax reforms, PLI expansion, and circular economy push
Ahead of the presentation of the Union Budget 2026–27, stakeholders across India’s solar and energy storage ecosystem have urged the government to focus on tax reforms, expansion of production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes with targeted allocations, faster viability gap funding (VGF) disbursements, additional funding for residential rooftop solar, improved access to long-term and affordable green finance, and a stronger push for circular economy initiatives and grid modernisation.