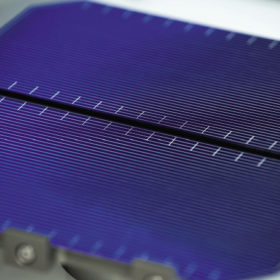
The long read: Laser focused
Solar manufacturing’s recent move toward larger wafer/cells throws into focus the need for effective cell-cutting techniques to handle the processing of these cells into half cut or even smaller formats. pv magazine looks at the landscape for cell cutting, as the technology reaches maturity and moves into the mainstream of cell/module production.
Covid-19: MNRE terms utility-scale solar power generation ‘essential service,’ allows related material and personnel movement
The ministry further announced waiver from section 144, Nationwide Lockdown, Curfew, or any other limitation on the number of people required for operation and maintenance of solar power plants. The directive came a day after lobby group National Solar Energy Federation wrote to the ministry asking for waivers.
Europe’s Wamtechnik, ION Energy partner to enable electric excavator
The European Li-ion battery manufacturer has partnered with the Mumbai based battery management system provider on the design and deployment of an electric excavator that would operate in subzero temperatures (below -20°C).
Sungrow signs 650 MW PV inverter supply deal with Avaada Energy
The Chinese inverter manufacturer will supply its 1500V 3.125 MW central inverter solution for Indian developer Avaada Energy’s upcoming PV projects in India.
Covid-19: Discom revenue dip could spell trouble for PV producers
Sliding electricity demand and declining commercial and industrial activity could prompt distribution companies to block or delay payments to solar power producers.
Prospects of India-UK partnerships in creating digitalized energy systems
India’s energy system immediately needs a shift from centralized commands to dynamic interactive structures. While the UK is already spearheading digitalization of its energy systems, India has ample areas demanding interventions, such as integration of decentralized energy systems using digital innovation and analytical tools.
India is third largest producer of electricity in the world: Power minister
The government has signed Memorandum of Understanding with Bhutan, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Myanmar to inter-alia improve power connectivity and enhance energy trading in the region.
SECI tenders another 32 MW (AC) solar projects for SCCL
The solar panels shall be installed on the coal miner’s over burden (OB) dump at Ramagundam (22 MW) and Dorli (10 MW) sites in Peddapalli district of Telangana. Bidding closes on April 22.
Pumped electricity storage makes a comeback in India, and the world is taking note
India’s energy storage juggernaut is on a roll with the country discovering the cheapest renewables cum storage tariff in history, anywhere in the world. The technology chosen is pumped storage. And by setting up an enabling environment, the government has signalled its commitment to boosting the market!
The long read: The research behind dust mitigation
Solar PV is surging in the Middle East, due to its sustainability and decentralized nature. But with the ample sunlight of the region comes fine dust, which can sharply reduce power output. Zulfa Rasheed from the Rochester Institute of Technology in Dubai looked at the latest research in the field and found that module-glass coating and robotic solutions appear to be the most promising options when it comes to dealing with dust.