The long read: Production ambitions
While China hosts the lion’s share of production capacity for solar modules, many other parts of the world harbor the ambition to build manufacturing industries of their own. Italy’s Ecoprogetti is building production lines all over the world in 2019, and pv magazine had the chance to catch up with the family-owned company’s CEO Laura Sartore, who sees India and the Middle East as the key markets for the PV production equipment business.
Jinko: ‘The days of mono will soon be behind us’
A spokeswoman from the Chinese manufacturer of the Swan series of double-sided solar panels says monofacial modules will soon be consigned to residential use as the price gap between them and higher-yielding bifacial products rapidly closes.
SECI retenders 97.5 MW rooftop solar projects for government buildings
Global bids are invited for RESCO and CAPEX mode grid-connected projects to be set up in different states and union territories of India. The projects shall be eligible for achievement-linked incentives. Bidding closes on September 30.
IndianOil to produce non-lithium EV batteries
The state-run fossil fuel giant has partnered with an unnamed foreign start-up to produce electric vehicle batteries using raw materials easily available in India.
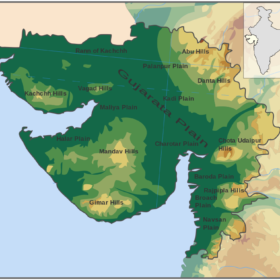
Gujarat may lead the renewables race by adding 4-5 GW annually: IEEFA
The state—which had 8.5 GW of renewables capacity (2 GW solar, 6 GW wind and 0.8 GW biomass) operational as of March—is expected to add a staggering 46 GW to reach 55 GW mark by 2029-30.
Australia shows the way forward for EVs in nations with vast distances
The Australian Renewable Energy Agency will contribute $15 million towards a planned nationwide network of ultra-fast charging stations that could show the way ahead for electromobility in India.
Manufacturing-linked mega tender set for more tweaks
Bidders interested in competing for a tender which will allocate 6 GW of solar capacity linked, pro rata, with 2 GW of manufacturing output now have until September 11 to register their bid as administrator the Solar Energy Corporation of India will amend the exercise to incorporate developer feedback.
Jharkhand tenders 10 MW rooftop solar EPC job for government buildings
The projects—to be set up on RESCO model (capital expenditures covered by the installer)—would come up on a total of 100 various government and private consumer buildings across the State.
West Bengal could get 1.7 GW of solar but coal will reign for at least 30 years
A minister said an unnamed private investor had proposed an 800 MW solar project in the state on top of a 900 MW scheme being carried out with Japan. But the chairman of power giant NTPC said AI and digitization should be used to extend coal burning for decades to come.
The long read: Floating PV to rise to GW scale in India
Tenders have begun to drive next-generation solar and storage applications in India. And as developers, administrators and asset owners become more familiar with the technology, the advantages of PV on water and in battery storage are driving the emergence of a pipeline of projects. Surbhi Singhvi, manager of consulting for Bridge to India, discusses the outlook and challenges for both applications.