Tata Power Renewables installs 1 GWp rooftop solar capacity in 9M FY2026
Tata Power Renewable Energy added more than 1 GWp rooftop solar capacity within the first nine months of FY26—a 125% YoY growth over 444.78 MWp installations achieved in the corresponding period of FY25.
India’s 2025 renewable energy sector review: Key highlights and way forward
With record 40+ GW solar and wind installations (solar: 34.9+ GW, wind: 5.8+GW), 2025 has marked yet another high point in Indian annual renewable capacity additions. The capacity additions have been driven by strong project momentum across all solar segments.
Taiwan on track to deploy 31.2 GW of solar by 2035
UK-based GlobalData says Taiwan is on course to more than double its current solar capacity by the end of 2035.
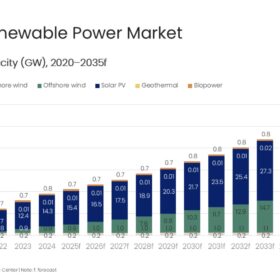
India’s energy transition has shifted gears decisively
India is moving decisively beyond capacity addition toward system-level maturity. Expanded transmission planning, a more diversified energy mix and better regulatory clarity signal a market design that is becoming ever more dynamic and future ready.
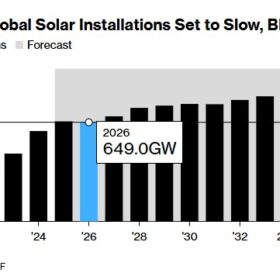
BNEF flags potential global solar slowdown in 2026 as China cools
BloombergNEF (BNEF) projects a slight year-on-year dip in global solar additions in 2026 as China’s growth eases, even as installations elsewhere continue to rise.
Why Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities will drive India’s next big solar jump
Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities are no longer behind in the solar journey, they are becoming the main growth drivers. With better government support, easier net-metering rules, and more awareness about savings, people in smaller cities are now ready for rooftop solar in a big way.
Sachin Tendulkar invests in solar EPC firm Suntek Energy
Cricket legend Sachin Tendulkar has invested INR 3.6 crore in Hyderabad-based solar EPC company Suntek Energy Systems, acquiring a 2% stake in the firm.
India surpasses 132 GW of installed solar capacity: MNRE
Solar PV capacity addition is led by Rajasthan, which accounts for 27% (36 GW) of the cumulative installed capacity. Gujarat ranks second with 24.8 GW, followed by Maharashtra with 17.2 GW. Together, these three states account for over 58% of India’s total installed solar capacity.
Why EPC leaders must diversify across energy transition and digital infrastructure
The EPC organisations that choose to lead across both the energy transition and digital infrastructure will not simply respond to the coming decades of change, they will shape them.
GEON launches inverter with inbuilt lithium battery for homes
GEON, part of the 60-year-old Kabra Extrusion Technik Group, has launched GELITHIUM, an all-in-one power backup system that integrates a pure sinewave inverter with an inbuilt lithium-ion battery. GELITHIUM is available in 1,250 VA and 2,500 VA variants, with 12.8V/100Ah and 25.6V/100Ah lithium batteries, respectively.