ISA Assembly approves payment guarantee mechanism for solar projects in Africa
The fifth assembly of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) approved Solar Facility, a payment guarantee mechanism to mitigate risks associated with solar projects in Africa.
Aerocompact launches high-elevation mounting system for rooftop PV
Portuguese startup Solarud has unveiled the next generation of its water-draining device for PV panels with low, sloping inclines. The new design avoids clogs caused by sand and dust, in nano and customized versions that fit installations and modules of different sizes.
Wind, solar payback times under a year in some parts of world, says Rystad
Record energy prices, particularly in Europe, are driving demand for renewables and energy storage. That is changing the equation for utility solar and wind investment and shortening project payback times to under a year in some regions. Storage deployment, driven by recent policy developments around the world, is also expected to get a big boost through to 2030.
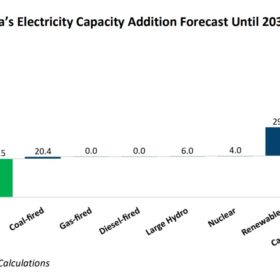
India expected to annually deploy 35-40 GW of renewables until FY2029-30 end
Ambitious government targets and commitments by both private and state-owned companies will propel renewable energy installations.
Tata Power targets 10 GW of renewables portfolio in Rajasthan in next five years
Tata Power is looking to expand its renewable power portfolio in Rajasthan to 10 GW in the next five years, from around 5 GW at present. It will also set up solar manufacturing units in the state.
Livguard unveils wall-mountable inverters for residential solar
India’s Livguard Solar has unveiled single-phase, grid-interactive inverters in rated power outputs of 3 kW and 5 kW, and efficiencies of 97.7% and 98%, respectively.
India installed 2,520 MW of rooftop solar in the twelve months ending June
The nation added 2,520 MW of rooftop solar in the twelve months ending June 30, 2022, taking the cumulative rooftop installations to 10,221 MW.
New solar tiles from Germany
Creaton and Autarq have developed a modular solar tile for complex rooftops. The product is reportedly compatible with all common PV inverters.
India’s residential rooftop solar capacity expected to rise by 60% this fiscal year
India’s cumulative residential rooftop solar capacity may rise by 60% to reach 3.2 GW by March 31, 2023 driven by rising consumer demand coupled with strong government support.
How long do residential solar inverters last?
Multiple factors can affect the productive lifespan of a residential solar inverter. We take a look at solar inverters in the second part of our ongoing series.