The Hydrogen Stream: US awards $34 million to 19 hydrogen projects
As the US and British government press ahead with their hydrogen support projects, a team from Korea and the US has developed an iridium nanostructure catalyst, which decreased the amount of the chemical element. Meanwhile, hydrogen projects are proceeding in West Virginia, Denmark, Finland, and Japan.
The Hydrogen Stream: Perovskites-based photoanodes for photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting
A research team has developed OHP-based photoanodes for photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting, minimizing the usual limitations. Meanwhile, China released its first hydrogen guideline, and Germany announced €18.6 billion for the hydrogen industry. Finally, a German company finds out that hydrogen trains are more expensive than battery-operated vehicles.
India needs 60-100 GW of electrolysis capacity to meet 5 MMT per year green hydrogen target
India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission targets the development of 5 million metric tonnes of green hydrogen production capacity per annum by 2030, which would require the nation to install 60-100 GW of electrolyzer capacity.
Adani New Industries Q1 revenue up 209% YoY
Adani New Industries Ltd recorded a revenue of INR 1,898 crore ($229 million) in the first quarter of FY 2023-24, 209% up year-on-year. Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) increased 7.5 times to INR 355 crore as export volumes surged 19 times.
The Hydrogen Stream: Germany to use hydrogen ‘in all sectors’
The German authorities have announced plans to double domestic electrolysis capacity to 10 GW by 2030, BloombergNEF has reported that green hydrogen became competitive with gray hydrogen earlier than expected, and Chinese researchers have presented new research on microbial hydrogen production.
GreenH building 1 GW electrolyzer fab in India
The company’s manufacturing plant in Haryana will produce proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyzers based on the technology from its Spanish parent firm H2B2 Electrolysis. The plant will start production by October.
The Hydrogen Stream: EU, Argentina, Chile, Uruguay to partner on hydrogen
The European Commission and the European Investment Bank have agreed to collaborate with Argentina, Chile and Uruguay on hydrogen, while Masdar, Mitsubishi and Inpex have said that they will use green hydrogen to produce e-methane and polypropylene.
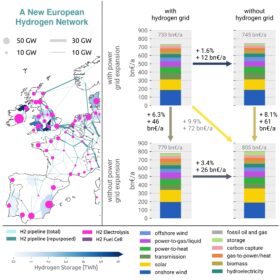
The Hydrogen Stream: Hydrogen grid could cut Europe’s energy costs by 3.4%
German researchers say gas-grid retrofits for hydrogen transport, combined with power grid expansion, could decarbonize Europe’s economy, while S&P says the global ammonia trade could expand by nearly 10 times by 2050.
The Hydrogen Stream: Scientists use perovskite compound to store ammonia
Japanese scientists have developed an organic-inorganic halide perovskite compound for the chemical storage of ammonia (NH3), while Bosch is preparing to exhibit new products in the hydrogen value chain.
Hild Electric signs 600 MW alkaline electrolyzers deal with NTPC
NTPC, India’s largest power company, will use Hild Electric’s green hydrogen production technology to decarbonize energy, transport and ammonia projects.