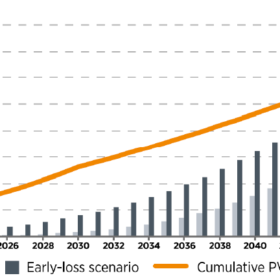
IEA PVSP predicts high-cost, low-revenue scenario for solar recycling
A recent report by the International Energy Agency Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme (IEA PVSP) reviews the current regulatory and industrial landscape for end-of-life PV management in Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Japan, South Korea, China, Australia, and the United States.
Saatvik joins PV Cycle initiative for solar waste recycling
Indian manufacturer Saatvik has joined Belgium-based PV Cycle’s recycling scheme for damaged solar modules.
Metastable opens innovation center for metal extraction from dead lithium batteries
The urban mining startup has set up an R&D and innovation center focused on improving the efficiency and yield of its chemical-free technology for extracting valuable materials from dead lithium batteries. It will ramp up the facility to double it up as a fully operational metal extraction unit by the end of December.
Industrial process for ‘mobile’ solar module recycling
German company Flaxres has developed an industrial process to recycle PV modules, and has begun operating a pilot facility at its new site where 10 tons of solar modules can be recycled daily. Flaxres plans to make equipment based on this facility available to international customers.
India will have 125 GWh of lithium batteries ready for recycling by 2030
India will see a cumulative demand for around 600 GWh of lithium-ion batteries from 2021 to 2030 across all segments. The recycling volume coming from the deployment of these batteries will be 125 GWh by 2030.
There’s big money in recycling materials from solar panels
Recycling solar panels keeps them out of landfills, but also provides much-needed raw materials with Rystad Energy projecting a value approaching $80 billion by 2050.
Recycling options for PV panels, batteries could drive circular economy, says NREL
Renewable hardware that lasts longer and uses fewer materials could bolster recycling efforts and help to build an effective circular economy for solar and battery technologies, says the US National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
BatX Energies raises $1.6 million to expand battery recycling
Vikrant Singh, co-founder and CTO of BatX Energies, told pv magazine that the company would use the funds to scale up its capacity, with plans to launch material production from end-of-life lithium batteries on a commercial scale. It will also set up recycling units in different geographies to locally produce black mass – a mixture of battery anode and cathode materials – and ship it to its India facility for battery material extraction.
Hinduja Group invests in UK second-life battery storage specialist
Hinduja Group, an Indian multinational, has invested GBP 15 million (($18.4 million) with four other investors in Connected Energy, a developer of energy storage systems based on second-life electric vehicle batteries. The investment will help Connected Energy to scale up its operations and move into utility-scale project development.
Used Audi e-tron batteries to power rickshaws in India
Battery startup Nunam is working with German carmaker Audi AG and the Audi Environmental Foundation to roll out electric rickshaws powered by used Audi e-tron used batteries. It expects to launch the e-rickshaws in India at some point early next year.