India imposes 25% safeguard duty on solar imports
The Indian government has imposed a safeguard duty of 25% on solar imports from China and Malaysia for two years. The Ministry of Finance (Department of Revenue) levied the duty based on the final recommendations proposed by the Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR). While most industry players are dismayed, believing project costs could “immediately” go up by 15%, others are more optimistic.
India’s trade war will have global repercussions
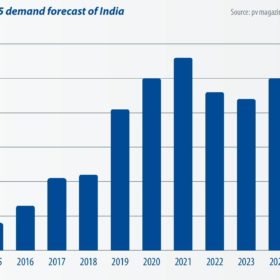
India is currently the second largest market in the world for PV module demand. With China’s domestic demand frozen since the 31/5 notification, the country’s total module demand in 2018 will likely only achieve 32-34 GW. This will allow India, which may surpass 10 GW in annual demand, to reach 13% of global PV demand this year. As a result, the future of India’s trade war has become an influential factor in the global PV industry.
Solar is turbocharging Karnataka to renewables leadership
The remarkable 4 GW of solar capacity added last year has seen the state displace Tamil Nadu as the nation’s renewables top dog. And there is more to come, according to a new report, with PV set to account for a third of rising energy demand over the next decade.
Global off-grid renewable capacity tripled between 2008 and 2017
While Africa has emerged as a dynamic, fast-moving hub, Asia leads in capacity deployment with its total capacity more than tripling to nearly 4.3 GW in 2017 from 1.3 GW in 2008, finds IRENA. Particularly, in India, a strong policy has pushed deployment of off-grid solar for agriculture and public end-uses.
EU MIP decision to have more effect on Indian PV market than safeguard tariffs
The proposed safeguard tariffs on imports from China and Malaysia are expected to generate a number of painful short-term impacts. Overall they are not expected to change much in the market, however, says TrendForce. What will have a bigger effect is the EU’s final MIP decision, due in September.
Azure Power wins 300 MW project to surpass 3 GW portfolio
The independent power producer has continuously expanded its project pipeline, routinely winning multimegawatt tenders. The latest winning bid relates to a pending PPA at Rs2.64 per kWh.
Government body recommends 25% tariff on Chinese and Malaysian cells and modules
Phased import tariff would fall to 20% 12 months after introduction and 15% for final six months of a proposed two-year period. Industry watchers say the cost of Indian solar energy could rise by up to 30%.
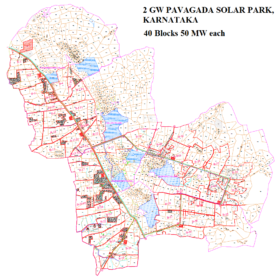
Tata Power wins 250 MW solar project in Karnataka
Tata Power Renewable Energy Ltd (TPREL), an arm of Tata Power, has won a contract to develop 250 MW (50 MW x 5) of solar projects in Tumkur district of Karnataka.
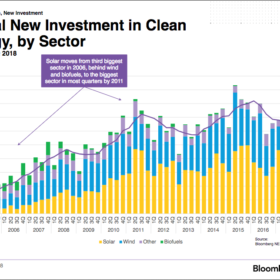
Global solar investment drops due to low project costs, China policy change
While overall global investment in clean energy saw a decrease of just 1% YoY in the first half of 2018, solar’s share dropped 19% following changes to China’s PV policy and lower project costs, says Bloomberg NEF (BNEF). It forecasts this trend to continue throughout the year.
Lower module pricing will bolster PV deployment in India
More than 80% of India’s solar equipment requirements are met through imports from China. Against this backdrop, industry analysts see the predicted 30% lower module pricing, following China’s revised policy, as a good news for Indian PV projects.