India introduces ‘Battery Aadhaar’ system to track EV batteries across lifecycle
India’s Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has released draft guidelines for the implementation of a Battery Pack Aadhaar system—an indigenous digital identification and data storage mechanism designed to ensure end-to-end lifecycle traceability of batteries, particularly those used in electric vehicles (EVs).
Bridging the gap between India’s rare earth reserves and extraction challenges
While India has research capabilities across public laboratories and academic institutions in both rare earths and battery recycling, the transition from lab-scale innovation to industrial deployment has been slow. This gap between research and commercial execution continues to limit scale across the critical minerals ecosystem.
Japan plans to tighten laws around large-scale solar
Japan is set to impose stricter environmental oversight on future large-scale solar projects. The government may also discontinue financial support under its feed-in tariff and feed-in premium schemes for large, ground-mounted solar beginning April 2027.
AGEL tops Global Green Utilities Rankings by UK-based Energy Intelligence
Adani Green Energy Ltd (AGEL) has claimed the top spot in the latest Energy Intelligence Top 100 Green Utilities ranking, pushing past China’s National Nuclear Corp. and Spain’s Acciona.
Revival of Nature-based Solutions (NbS) in 2025
The IUCN’s updated Global Standard, growing debate on finance, and stronger emphasis on rights and monitoring mark a transition from hopeful experimentation to disciplined scaling. If the next year invests in credibility and the scaffolding that turns pilots into pipelines, Nature-based Solutions could finally become a practical pillar of climate, biodiversity and development strategies worldwide.
Attero announces INR 150 crore investment to expand e-waste and copper recycling capacity across India
Once the new plants are commissioned, Attero’s overall processing capacity across e-waste and metals recovery will reach 244,000 tonnes per annum.
The future of impact funding: Aligning capital with sustainable outcomes
The largest area of green financing is energy-efficient machinery, which supports MSMEs in modernising production lines and reducing operational energy consumption. Significant capital is also being channelled into rooftop solar installations, electric vehicles, and enterprises operating in the water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) sectors, across clusters such as manufacturing, healthcare, and food processing.
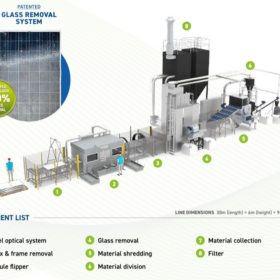
Jakson to set up high-tech solar PV module recycling line in partnership with Europe’s Ecoprogetti
Jakson Engineers Ltd will set up a high-tech solar PV module recycling plant capable of recycling around 5,00,000 PV modules, or approximately 13,500 tonnes of modules per year, recovering critical materials and enabling responsible end-of-life solar management. The recycling line will be supplied by Ecoprogetti.
Renewables’ share in Indian textile industry’s total power consumption rises
The average share of renewable energy in the Indian textile industry’s total energy consumption increased from about 14% in FY2023 to nearly 18% in FY2025, according to a new report from ICRA ESG Ratings Ltd.
From waste to wealth: Circular strategies driving a sustainable India
The promise of India’s circular economy lies in its ability to turn environmental challenges into engines of growth. Achieving it will take investment, innovation, and clear ways to measure progress.