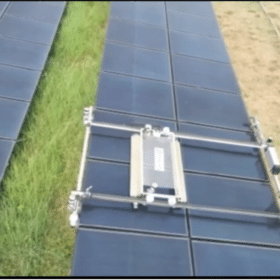
Solar panel cleaning startup Solavio Labs selected into Canadian accelerator program
The Coimbatore-based startup has designed an autonomous solar panel cleaning bot with a modular design, making it compatible with almost any structure, mounting area, or climatic condition.
The unstoppable trajectory of photovoltaic water pumps
Scientists in Russia have analyzed the most important technological advances achieved for solar water pumps over the past decades and have indicated the roadmap that future research should follow to expand their use and application.
SECI tweaks 100 MW solar-plus-storage Chhattisgarh tender
The Solar Energy Corporation of India has issued amendments to the procurement and extended the bidding deadline a second time.
India, Sweden to fund joint R&D in smart grids
India’s Department of Science & Technology and the Swedish Energy Agency have launched a collaborative funding program for Indian and Swedish companies that aim to jointly develop new technologies, services and processes in the area of smart grids.
Rooftop PV vs. rooftop farming
U.K. researchers have developed a way to optimize urban rooftop use with solar PV and agriculture.
Mounting structure for balcony solar modules
Sino-Australian manufacturer Clenergy has unveiled a new mounting solution for PV panels installed in balconies. The structure is adjustable to different types of commonly-sized balconies with metal railings.
The future of cars is electric – but how soon is this future?
According to a new report by BloombergNEF, 58% of global passenger vehicle sales in 2040 will come from electric vehicles, yet they will make up less than 33% of all cars on the road.
BHEL tenders for supply of 286,000 solar cells
Manufacturers have until December 4 to bid for the supply of 286,000 multicrystalline silicon solar cells using five bus bars. The cells are required in the peak power rating of 4.62W (10,000 quantities), 4.67Wp (60,000) and 4.72Wp (216,000).
India and Israel to work together on perovskite solar cells and lithium sulfur batteries
Low-cost batteries and novel perovskite materials are among the topics selected for joint research and development.
Even if organic PV is cheap enough, efficiency does matter
A British-German research team claims that organic PV technologies may become mature enough to compete with crystalline silicon and thin-film products not only in BIPV, but also in power generation in the electricity market. In order to get there, however, organic PV products will have to achieve higher efficiencies.