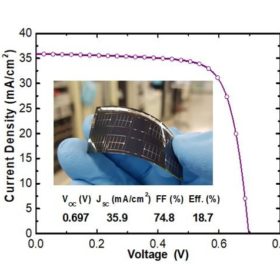
Korean researchers announce flexible CIGS solar cell with 20.4% efficiency
The thin-film cell was manufactured through a low-temperature process and doping with alkali elements.
A plug-and-play solar-powered battery back-up solution for the home
The OneBox, from Indian manufacturer Vision Mechatronics, consists of a lithium battery, hybrid inverter and solar charge controller to give a hassle-free solution for electricity back-up during power outages. Solar rooftop owners are offered a grid feed feature to maximize net metering income from any excess power generated.
Integrating stress and temperature sensors in crystalline silicon cells
Fraunhofer ISE researchers have integrated stress and temperature sensors within a PV module. They claim that the devices cover a very minimal part of the cells, and that their interaction with the module and the cell itself is quite limited. The sensors can be manufactured as part of a regular cell manufacturing process.
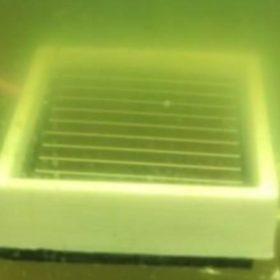
How do solar cells work underwater?
Although cells lose much of their power yield when submerged, they may not be useless. Researchers in India say submerged cells could be used in monitoring sensors and for other commercial and defense applications. An amorphous silicon cell from Panasonic was tested in their study.
Self-healing polymeric coating for photovoltaic devices
A new polymer developed by Indian researchers can mend its own cracks when exposed to ultraviolet light. The unique ability makes it an ideal candidate as a smart coating for photovoltaic solar devices to prevent damages and increase performances.
Assessing the impact of micro-cracks in solar glass
A Turkish research team has analyzed how big changes in temperature can affect absorbance, light transmittance and reflectivity in two types of solar glass. The scientists demonstrated lower efficiency in solar cells and the glass itself were attributable to a large number of micro-cracks and deformations on the glass surface.
Raising crops in PV facades
An international research group has analyzed the visual impact of PV facades on buildings which include crop cultivation. Architects, PV specialists and farmers were surveyed and the results showed broad acceptance of such projects.
Bridging the gap between battery and supercapacitor
By engineering the structure of a hard carbon electrode, scientists at the CIC energIGUNE research center have created an ‘ultrafast battery’ which has been shown to combine the energy density of a lithium device with the fast discharge times normally associated with supercapacitors.
Healing the cracks for a more stable perovskite
Scientists in the United States have demonstrated simple methods for ‘healing’ the cracks that form in perovskite solar cells. While it is far from clear how the approach could be applied commercially, the work suggests possibilities for maintaining the performance of perovskite cells in long-term operation.
Solar powered portable cold storage, grid monitoring system among winners of Social Alpha Energy Challenge 2.0
The winning startups will receive lab-to-market incubation support at the Clean Energy International Incubation Centre (CEIIC), which has been set up by the not-for-profit platform Social Alpha with support from Government of India and Tata Trusts in Delhi.