The long read: PV’s Polish cold turkey
Considering the remarkable advances made by the solar sector since the Rio ‘Earth Summit’ of 1992, PV was notable by its absence at the Convention of Parties climate change summit held by the UN in Poland.
Thai solar imports soared more than 2,700% in nine months
From April to November, Indian imports of solar cells and modules from Singapore – worth Rs489 crore, Vietnam (Rs263 crore) and Thailand (Rs155 crore) recorded whopping annual growth rates of 242%, 440% and 2,711%, respectively.
Hanergy hits 24.34% efficiency on HJT cell
Chinese PV manufacturer Hanergy Thin Film Power Group today announced it has achieved 24.23% cell efficiency using its silicon heterojunction technology. The efficiency has been confirmed by Japan’s Electrical Safety & Environment Technology Laboratories.
South Korea kicks off polysilicon duty talks with China
At the Korea-China Free Trade Agreement Joint Committee meeting, the South Korean government urged China to lift import measures against its polyoxymethylene, optical fiber, polysilicon and grain-oriented electrical steel. China imposed duties on polysilicon from South Korea and the United States in July 2013.
China ready to set 3 GW quota for residential solar in 2019
Sources have told pv magazine the authorities are ready to restart the nation’s residential rooftop segment and have also agreed upon subsidy payments for other distributed generation and utility-scale projects.
This year could see a reckoning for ultra-mega PV projects
The fate of the clutch of 500 MW-plus projects due to break ground this year could determine whether such ambitious schemes have a viable future, says Wood Mackenzie in its solar 2019 forecast. And the Indian market should brace for consolidation, add the analysts, because of aggressive reverse-auction tariff pricing.
Hyper low costs ensure clean energy investment fell in India last year
The nation still managed to attract around $11.1 billion for renewable energy in 2018, to be the world’s fifth most attractive destination for funds, according to new figures compiled by BloombergNEF.
Indian solar is coming up on the rails of China and the US
Taiwanese market research company EnergyTrend says the 5/31 policy change in China last year had a less dramatic effect on global demand than expected and, with the Modi government introducing solar-friendly policies, India – and Japan – will close the gap on the world leaders for installed PV capacity.
China unveils an ambitious new push on grid parity solar
Beijing has outlined a series of policies mandating local and provincial authorities, state-owned banks and grid operators to pull out the stops to drive the rapid escalation of subsidy-free PV projects. The announcement has seen Chinese solar stocks on the rise.
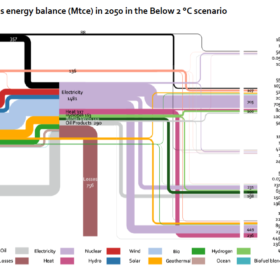
CREO 2018: A new era in the Chinese energy transition
A new era in the Chinese energy transition is on the menu and renewables are the order of the day, according to the latest China Renewable Energy Outlook (CREO). China will not require a gas bridge between coal and renewables, it finds, adding that renewables will become the core of the nation’s energy system by 2050, with annual PV installs of between 80-160 GW possible. Not only that, but electricity supply could be cheaper in this future than it is today.