Singapore’s Cleantech Solar secures US$75 million green loan from ING Bank
The commercial and industrial solar developer, which commands a significant share in the Indian market, will use the amount to fund rooftop PV installations for corporates across Southeast Asia.
Energy and Economy: Rewriting the Indian story for the World
India is running the world’s largest renewable energy expansion program with a mind-boggling target of 450 GW by 2030. Can the country with a growing energy demand do more than this? Can it do what developed countries should have done years ago?
The long read: Sink or swim
The impressive progress made by offshore wind arrays may be attracting a new group of PV developers looking to leave the constraints of the roof and free field behind. And while saltwater, wind and waves are no friend of PV, progress is being made in proving the potential applications.
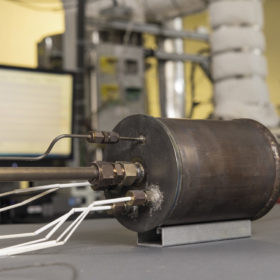
The long read: Scientists at Argonne develop new kind of thermal battery
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have developed a new kind of thermal battery that can greatly increase the energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness of many industrial processes and shows great promise for use in the solar industry. Liz Thompson reports that Argonne’s Thermal Energy Storage System (TESS) can rapidly capture and store surplus heat so that it can be used as needed. With its pioneering modular design and material advancements resulting in greater efficiency, TESS is a big step forward in thermal battery technology.
Supply chain concerns will drive EV battery recycling policies
With electric vehicles starting to gain traction, the International Energy Agency’s updated, ten-year e-mobility forecast has suggested geopolitical and economic concerns will trump environmental niceties when it comes to encouraging recycling. But what price ever-cheaper batteries?
The long read: Criteria and implications for gallium-doping
As a remedy for light-induced degradation (LID) in crystalline silicon cells, gallium-doped wafers are showing considerable promise. With reports that ingot growth productivity can rival that of boron doping, it seems that gallium doping may now be able to meet the cost, integration and performance criteria that have informed solar manufacturing technology adoption, writes Alex Barrows, senior research analyst at U.K.-based consultancy Exawatt.
Agrivoltaics works better with leafy greens, root crops
U.S. researchers have created a new model to assess the overlap between solar potential and underlying land use. The areas with the largest potential are the western United States, southern Africa, and the Middle East. The researchers concluded that croplands, grasslands, and wetlands are the top three land classes for PV projects linked to agricultural activities, while barren terrain, traditionally prioritized for solar PV system installation, ranked fifth.
Historic-low interest rates will power ahead astonishing solar cost reductions
An Ieefa report has suggested the cost of generating electricity from solar will be near zero in the world’s sunniest regions by 2030-40 – despite what the naysayers at the International Energy Agency might think.
Single-axis bifacial PV offers lowest LCOE in 93.1% of world’s land area
Researchers from the Solar Energy Research Institute of Singapore have concluded that utility-scale PV projects relying on bifacial panels and single-axis trackers deliver the lowest levelized cost of energy in most of the world. They found that the combination of bifacial products with dual-axis trackers is still too expensive, despite the higher yield. The second-lowest LCOE is offered by monofacial single-axis tracker plants.
The long read: New fuels, new powers
The energy transition will change the geopolitical landscape, which has hitherto observed closely who controls the production and trade of hydrocarbons. The current ambition to find alternative sources of power has given impetus to a growing academic community to determine the probable geopolitical outcome of the energy transition. Renewables do not mutually share most of the unique features of fossil fuels, which translate into power political effects. So how should we understand the world of tomorrow?