Interview: GoodWe talks IPOs, policy changes and tripling production capacity
In an interview with pv magazine, vice president of GoodWe, Ron Shen, talks about the company’s plans for Germany, Spain, Africa and India, in addition to its goal to triple production capacity to 15 GW in China. He also discusses the effect of China’s 31/5 policy change, and plans for an initial public offering (IPO).
The long read: A new test for trackers
The benefits of deploying bifacial solar panels on single-axis trackers are touted like snake oil these days, with promises of anywhere from 5 to 50% gains in energy output compared with a monofacial panel. Unfortunately, the field data that might delineate the actual energy gain of a bifacial panel on a tracker are hard to acquire, and the data that are available typically describe small-scale tests under tightly defined conditions.
US scientists create MPP algorithm to measure PV panel degradation
The algorithm is said to be able to examine the relationship between weather forecast data and the projection of electric circuit parameters. Through this innovation, Purdue University researchers claim they can interpret the routinely collected maximum power point (MPP) time-series data, to assess the time-dependent “health” of installed solar modules.
Researchers propose doubling today’s solar panel efficiency using two weird tricks
By double stacking a perovskite-silicon solar cell and using the cell in a glass-on-glass bifacial solar module, scientists model that a 30-36% efficient solar module can be attained.
PV demand, changing auctions and price declines – GTM lays out its latest predictions
An uptick in global PV demand will occur in 2020, with China’s 30.5 policy directly affecting 2018’s results by around 18%, says GTM Research. Rapidly falling module prices will benefit predominantly Asian markets, where modules comprise the lion’s share of capex, although regions like Europe will see increased installations. Laying out 10 PV predictions, it anticipates, among others, intensified competition, lower bid prices, more technology neutral auctions and an increasing amount of subsidy free solar.
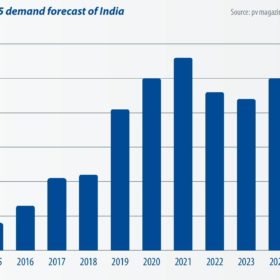
India’s trade war will have global repercussions
India is currently the second largest market in the world for PV module demand. With China’s domestic demand frozen since the 31/5 notification, the country’s total module demand in 2018 will likely only achieve 32-34 GW. This will allow India, which may surpass 10 GW in annual demand, to reach 13% of global PV demand this year. As a result, the future of India’s trade war has become an influential factor in the global PV industry.
Global off-grid renewable capacity tripled between 2008 and 2017
While Africa has emerged as a dynamic, fast-moving hub, Asia leads in capacity deployment with its total capacity more than tripling to nearly 4.3 GW in 2017 from 1.3 GW in 2008, finds IRENA. Particularly, in India, a strong policy has pushed deployment of off-grid solar for agriculture and public end-uses.
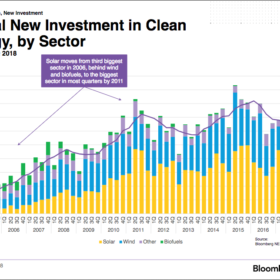
Global solar investment drops due to low project costs, China policy change
While overall global investment in clean energy saw a decrease of just 1% YoY in the first half of 2018, solar’s share dropped 19% following changes to China’s PV policy and lower project costs, says Bloomberg NEF (BNEF). It forecasts this trend to continue throughout the year.
President Elect, GSC talks about new ISA partnership, plans for global solar promotion
In a significant development, two major international solar coalitions – the Global Solar Council (GSC) and the International Solar Alliance (ISA) – signed an MoU for the cooperation and collaboration of solar growth in all ISA-member countries. Pranav Mehta from the GSC talks to pv magazine about the move.
Falling battery costs to push solar, wind to 50% electricity generation by 2050, but electricity still failing CO₂ reduction targets – BNEF
Solar PV capacity is set to grow 17-fold, and wind six-fold, by 2050, to account for nearly half of global electricity generation, predicts BNEF, while investments will reach US$11.5 trillion. Cost reductions will drive this charge, particularly in the battery market, which will benefit from the EV manufacturing ramp up. Despite this, the electricity sector is still failing to bring CO₂ emissions down to the required levels, with its continued dependence on gas.